Understanding Human Musculature: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
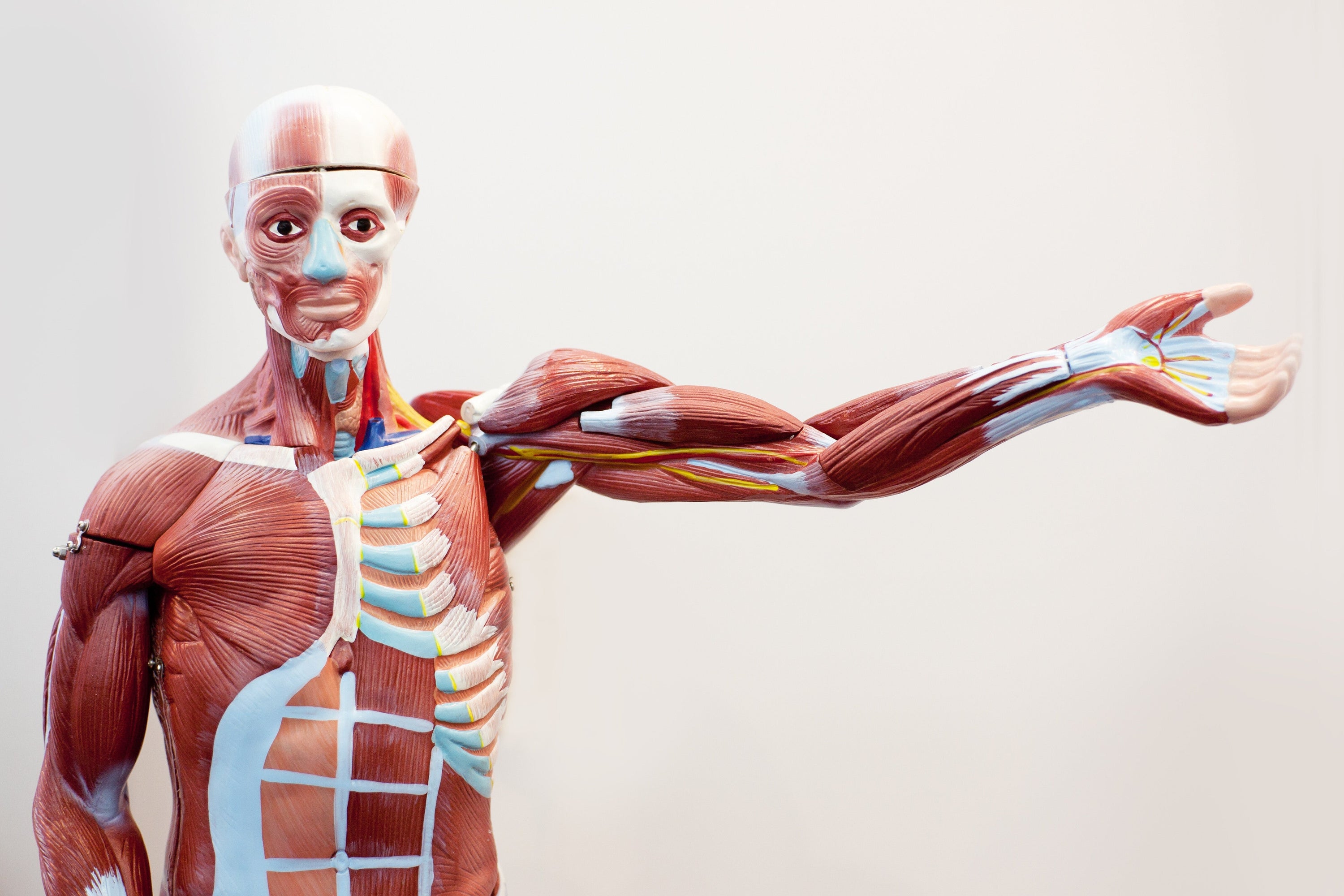
The human musculature is a complex system that plays a crucial role in most body movements and physiological processes. Understanding musculature is essential not only for medical students and healthcare professionals but also for fitness enthusiasts and patients interested in proper treatment and injury prevention. Learning about muscles with anatomical images offers a visual way to recognize and understand this fascinating system. Anatomical images provide detailed insights into the location, structure, and function of muscles.
Basics of Human Musculature
Human musculature can be broadly categorized into three types: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Each type of muscle has specific functions in the body:
- Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of hollow organs such as the stomach, blood vessels, and intestines. It controls processes like digestion and blood circulation in the background.
- Cardiac Muscle: A special form of muscle found only in the heart, responsible for maintaining a constant heartbeat.
- Skeletal Muscle: These muscles facilitate the movement of the skeleton and can be consciously controlled. They are typically what we refer to when we talk about "learning muscles." Skeletal muscle posters are a useful tool for this purpose.
Learning Muscles with Anatomical Images
Learning muscles with popular anatomical posters is an effective method to understand the structure of human musculature. This visual approach helps not only in memorizing the names and positions of muscles but also in gaining a better understanding of their functional significance in the body. Here are several ways to effectively learn human muscles using anatomical images.
Visualization of Anatomy Anatomical images are beneficial for accurately depicting human muscles, which might not be possible with the naked eye or by simply reading texts. They illustrate the exact location, size, and shape of all muscles and their parts. Visualization helps build a mental image of anatomical structures, which is especially advantageous for visual learners.
Understanding Relationships Between Structures Another advantage of learning muscles with anatomical images is the ability to comprehend the relationships between different muscles and between muscles, bones, tendons, and other structures. This knowledge is crucial for understanding how various parts of the body work together to create movement.
Facilitating the Learning Process Learning muscles can be challenging due to the large number of muscles and the complexity of their functions and interactions. Anatomical images, such as those depicting sports activities, can simplify the learning process by visualizing complex information in a clear and straightforward manner. Color coding, labels, and interactive elements help organize and convey information effectively.
Promoting Active Muscle Learning Active learning of anatomy muscles is encouraged through the use of anatomical images. By viewing and analyzing images, drawing muscles, and describing their parts, you can develop a better understanding of the material. These activities enhance long-term memory and make it easier to apply knowledge in practice.
Adapting to Different Learning Styles Since everyone has their own learning style, anatomical images offer a versatile learning method that meets various needs. Whether through viewing, drawing, or using digital models, muscle learners can choose the approach that best suits their style to learn muscles effectively.
Learning Muscles – Patient Education in Practice with Anatomical Images
Patient education is a crucial aspect of medical practice. It helps optimize patients' understanding of their health conditions, treatment options, and preventive measures. Anatomical images play a significant role here, providing a visual foundation on which complex information can be clearly presented.
Visualization of Diagnoses Anatomical images enable doctors to illustrate diagnoses. By seeing where a problem lies, patients can better understand their health situation. This contributes to active participation in the treatment process and helps reduce fears or misunderstandings.
Explanation of Treatment Procedures Whether conservative treatments, physiotherapy exercises, or surgical interventions, anatomical images can help explain the purpose, process, and outcomes of a treatment. By examining images that visualize how and why a specific treatment works, patients can make informed health decisions.
Promoting Prevention In addition to their use in diagnosis and treatment, anatomical images are a powerful tool for conveying preventive measures. By understanding how certain lifestyle habits can affect musculature and other body parts, patients are inspired to live healthier lifestyles.
Supporting Rehabilitation During the rehabilitation phase, anatomical images are valuable for explaining the importance of physiotherapy exercises and other rehabilitation measures to patients. Understanding the anatomical basis of their exercises helps patients perform them correctly, leading to optimal recovery.
Improving Compliance By understanding their medical situation, patients are more likely to follow their doctors' recommendations. Anatomical images can promote this understanding by making complex concepts comprehensible. This improved compliance leads to better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
Learning Muscles – Our Recommendation
Continuing education in muscle learning with anatomical images is essential for gaining a precise understanding of the human body. Anatomical images are a crucial tool for both medical professionals and patients to grasp anatomical and physiological connections. At Animus Medicus, we offer a wide range of high-quality anatomical images designed specifically for learning muscles. These resources are a great investment for anyone looking to expand their knowledge of musculature. Additionally, we offer a variety of extras such as medical socks, anatomy phone cases, and anatomy pins, as well as anatomical jewelry. Feel free to visit our website to explore our offerings.